|
Il
Global Positioning System (GPS) funziona sul principio che se si
conosce la distanza da diverse localitÓ, quindi Ŕ possibile calcolare
la posizione. I luoghi noti sono i 24 satelliti situati in sei piani
orbitali a quota 20,2 mila chilometri. Questi satelliti intorno alla
terra ogni 12 ore e trasmettono un flusso di dati alla frequenza L1
primario 1.575GHZ che porta la grossa acquisizione (C / A) segnale
codificato al suolo. Il ricevitore GPS misura il tempo di arrivo del
codice C / A ad una frazione di un millisecondo, e quindi determina la
distanza al satellite.
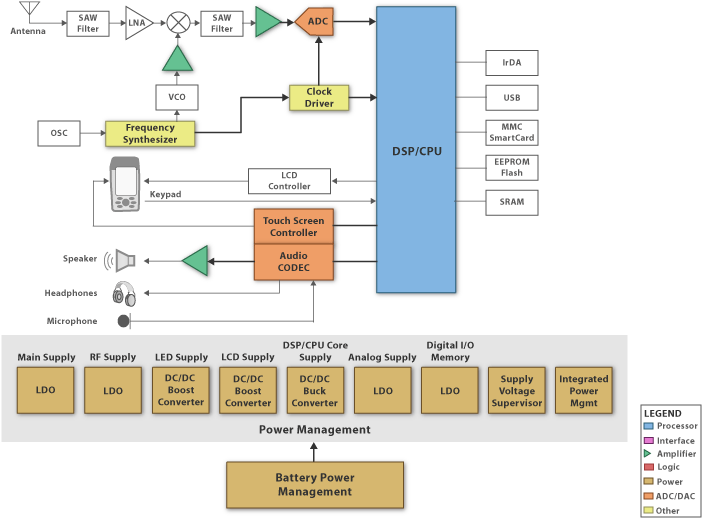
The Core Subsystems include:
-
Front End
- the GPS L1 signals (Maximum = 24 signals) at 1.575GHz are received at
the antenna and amplified by the Low-Noise-Amplifier (LNA). The RF
front-end further filters, mixes, and amplifies (AGC) the signal down
to the IF frequency where it is digitally sampled by a ADC. ' -
Baseband Processor/CPU
- the ADC samples of GPS C/A code signals are correlated by the DSP and
then formulated to make range measurements to the GPS satellites. The
DSP is interfaced with a general-purpose CPU, which handles tracking
channels and controls user interfaces. TI OMAP integrates both DSP and
ARM processor on the same chip.' -
Memory
- the processor runs applications stored in memory. The OS is stored in
non-volatile memory such as EE/FLASH/ROM. Applications may be loaded in
FLASH or DRAM. ' -
User Interface
- allows user to input/output data from the receiver using input
commands via microphone, touch screen, and output MP3 to the earplug.' -
Connectivity - allows the receiver to connect to the USB port.'
-
Power Conversion - converts input power (battery or wall plug) to run various functional blocks.
|
|