|
|
|||
MOTORI AC - 4
|
|||
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
Capacitor Start/Capacitor Run AC Induction
Motor
This motor has a start type capacitor in series with the auxiliary
winding like the capacitor start motor for high starting torque. Like a
PSC motor, it also has a run type capacitor that is in series with the
auxiliary winding after the start capacitor is switched out of the
circuit. This allows high overload torque. FIGURE
7: TYPICAL CAPACITOR START/RUN INDUCTION MOTOR
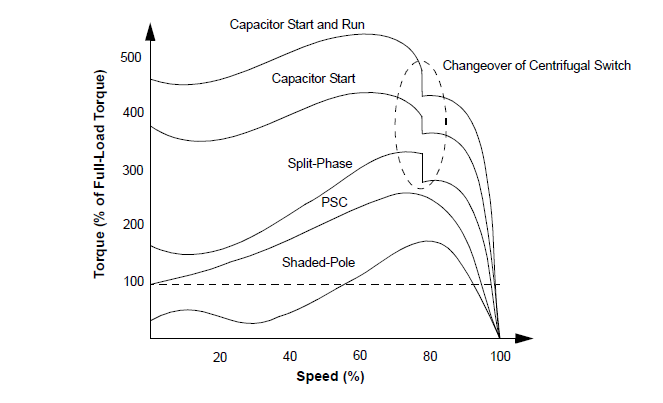
This type of motor can be designed for lower full-load currents and
higher efficiency (see Figure 9 for torquespeed curve). This motor is
costly due to start and run capacitors and centrifugal switch. It is
able to handle applications too demanding for any other kind of
single-phase motor. These include woodworking machinery, air
compressors, high-pressure water pumps, vacuum pumps and other high
torque applications requiring 1 to 10 hp.Shaded-Pole AC Induction Motor
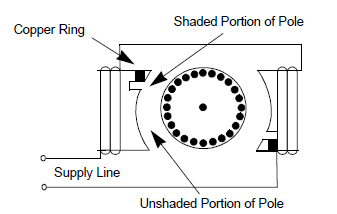
Shaded-pole motors have only one main winding and no start winding. Starting is by means of a design that rings a continuous copper loop around a small portion of each of the motor poles. This “shades” that portion of the pole, causing the magnetic field in the shaded area to lag behind the field in the unshaded area. The reaction of the two fields gets the shaft rotating. Because the shaded-pole motor lacks a start winding, starting switch or capacitor, it is electrically simple and inexpensive. Also, the speed can be controlled merely by varying voltage, or through a multi-tap winding. Mechanically, the shaded-pole motor construction allows high-volume production. In fact, these are usually considered as “disposable” motors, meaning they are much cheaper to replace than to repair
FIGURE 8: TYPICAL SHADED-POLE INDUCTION
MOTOR
The
shaded-pole motor has many positive features but it also has several
disadvantages. It’s low starting torque is typically 25% to 75% of the
rated torque. It is a high slip motor with a running speed 7% to 10%
below the synchronous speed.
FIGURE
9: TORQUE-SPEED CURVES OF DIFFERENT TYPES OF SINGLE-PHASE INDUCTION MOTORS
|
|
||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||